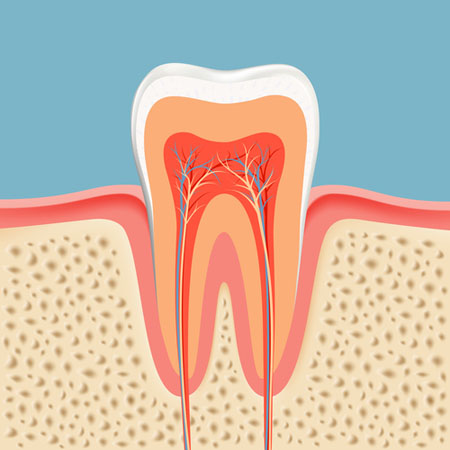
Pulp Trivia
It’s no secret that root canal therapy (RCT) saves your natural teeth by removing infected pulp. What exactly is dental pulp, though? It’s a lot more important than you may realize — keep reading for some pulp trivia!
Fact #1
Pulp is the living part of the tooth. It’s made of nerves, blood vessels and connective tissue that feed the tooth vital nutrients to keep it “alive,” or healthy and functioning.
Fact #2
Dental pulp is your tooth’s alarm system. When something goes wrong with your teeth, such as trauma or decay, the pulp experiences pressure and sensitivity changes that you perceive as pain.
Fact #3
The pulp is responsible for dentin formation. Dentin is the tissue layer beneath the enamel that protects the pulp. Because enamel is translucent, dentin is visible through the enamel and gives the tooth its color. Pulp contains cells called odontoblasts that initiate dentin creation.
Fact #4
The tooth can survive without pulp, but not with infected pulp. Pulp is a crucial part of tooth development, but once the tooth has fully matured, it can get nutrients from surrounding tissue and the pulp is no longer 100% necessary. However, infected tissue in a fully developed tooth can cause a lot of damage. This is why root canal therapy is necessary to save teeth that suffer pulp trauma.
Fact #5
Blood vessels and nerves in pulp are connected to gum tissue in the jaw. The apical foramen is a hole at the apex, or tip, or the tooth’s root. Blood vessels and nerves run from the jaw through the apical foramen and become part of the pulp once they enter the tooth.
Fact #6
Diseased gum tissue can cause pulp to become infected. Because blood vessels and nerves connect the gums to the pulp, diseased gum tissue can affect the pulp. Conversely, infected pulp can also spread and cause gum disease.
With all these functions of dental pulp in mind, it’s no wonder root canal therapy is such an important procedure! Call [PRACTICE_NAME] at [PHONE] to schedule a consultation if you’re having tooth pain and considering root canal therapy.
